Heard of the GLidD, "Oh, this is it."
Based on the context of society’s demands, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology has noted why companies often do not hire doctoral graduate students. This context explains, for example, that such students want to work only in their own specialized fields and have less motivation to explore other options, have low communication skills, or lack leadership skills. From the start, the HBP established its diploma policy to reflect society’s demands, mentioning the need for communication and leadership skills. However, at first, I did not understand how students would be able learn these skills or how we could confirm their learning in the new graduate school education program in the Leading Programs in Doctoral Education project.
Around that time, I heard of the GLidD, and immediately thought, “Oh, this is it.” Until now, graduate school education has consisted of credit-awarding, subject-based learning and a dissertation based on research. This structure allows students who have acquired expertise and necessary knowledge through course learning and research to earn a degree. However, the structure makes it difficult to evaluate whether students have also acquired communication skills.
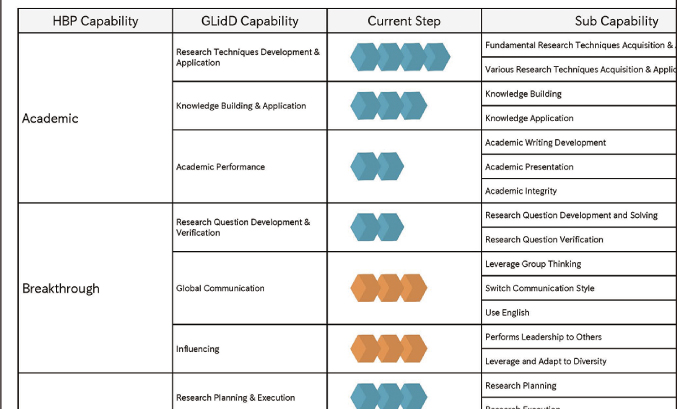
Additionally, there are various aspects of professional competence, for example, creating figures, writing papers, understanding research conducted globally across a wide range of topics when writing papers, or holding productive discussions with professionals in related fields. Moreover, to evaluate whether students have acquired communication skills, we also need to foster these skills step by step from one task to the next. I see the GLidD as a system that allows students to recognize where they stand and what their next goals are by visualizing their level of competence. I feel certain that this system can become the third pillar of postgraduate education, after subject-based learning and research.
Formative assessment report on GLidD
[ Program for Leading Graduate School ]
As the advancement of science and technology drives the development of society, expansion of knowledge brings about segmentation of specialized fields, it gets harder to capture the whole system and find certain value. Under these circumstances, it was necessary to raise high-level human resources who can overlook the whole framework beyond the boundaries of specialized fields and lead to solving social problems.
The Ministry of Education launches a business that supports radical reforms of graduate school education aiming to develop and deploy degree programs that get beyond the areas of expertise, to integrate the prior and later stages of doctoral course, and to make it hallmarked to the world, in order to bring out global, active in-industry-academic-government leaders who have wide overview and creativity.
Willing to take on more challenges
Research is generally at the center of graduate school activities. However, in the HBP, I can participate in a variety of activities and projects in addition to my research activity and meet people from diverse cultural backgrounds both on- and off-campus. Consequently, my horizons are expanding. I have actively benefitted from various opportunities that the HBP offers, and I am willing to take on more challenges by making the most of this program. I think that the HBP environment is very appealing. GLidD provides wonderful support for taking on greater challenges, allowing me to record what I have accomplished in the program and organize my own experiences through reviews and feedback given by teachers. Since GLidD is required for graduation, its objectives align with those required of students in the HBP. For example, when participating in internships and laboratory rotations, I refer to GLidD to organize skills and identify how I can anticipate growing through each experience.
The essential graduation requirement for GLidD is set as Step 2 or Step 3, but I think that it would be best to require it in Step 4 when HBP students are focused on becoming future professionals. The requirements of Step 4 are very difficult. Therefore, completing even one category in Step 4 represents progress toward the goal. Since it is difficult for a student to complete Step 4 in many categories, I respect people who can complete it in just one category, and I would like to work diligently to be one of them.

Active use of various contents in HBP
[ GLidD (Growth & Learning identification powered by Instructional Design) ]
It was necessary to develop new frameworks and systems to help students recognize their own learning outcomes and growth acquired through the practical educational programs such as oversea studies, internships and classes of discussion and project based learning.
The HBP introduced GLidD in order for quality assurance of academic degrees. GLidD is the formative assessment system which quantitatively assesses and certifies student’s transferable skills with evidence-based methods. In addition, HBP incorporated regular interview process to capture personal situation of students as holistic supports.

